F. A. Q.
Acne
curato da Anissa Westenberg
Perché ho l'acne?
L'acne è causata da una combinazione di quattro fattori: maggiore produzione di sebo, pori ostruiti, presenza di batteri specifici e infiammazione. La produzione di sebo è influenzata dagli ormoni, pertanto l'acne spesso si presenta durante la pubertà, ma può verificarsi a tutte le età Ciò avviene specialmente nelle donne poiché hanno più cambiamenti ormonali durante la loro vita. Non tutte le persone hanno la stessa quantità di acne perché i follicoli del sebo reagiscono in modi diversi ai cambiamenti del corpo.
È noto che l'acne è ereditaria: se uno dei tuoi genitori ha avuto l'acne, è più probabile che l'abbia pure tu. Anche stress e trattamenti per la pelle sbagliati possono peggiorare l'acne.
Spesso la causa specifica dell'acne non è chiara ed è difficile da determinare, tuttavia con il giusto trattamento, è possibile gestirla. (1,2)
Non sono più in pubertà, come mai ho ancora l'acne?
Durante la pubertà, gli ormoni fanno sì che la pelle produca più sebo, causando l'acne. Ma anche in momenti successivi, gli squilibri ormonali possono causare più acne. Questo succede molto nelle donne, ad esempio prima delle mestruazioni o durante la gravidanza. Lo stress, la pelle sensibile, i prodotti per la cura della pelle, il fumo, la dieta, alcuni farmaci e le malattie endocrine sono solo alcuni esempi di ciò che può peggiorare l'acne a qualsiasi età. (3,4)
Schiacciare i "brufoli" peggiora la situazione?
Nella maggior parte dei casi, è vero. Alcuni professionisti possono prendersi cura dei brufoli, ma farlo da soli peggiorerà quasi sempre la situazione. L´acne è la risposta del corpo a pori bloccati e batteri; l'infiammazione segnala che l'organismo sta cercando di curare la cute.
Invece di fare progressi, rischi di spingere i batteri e l'olio ancora più a fondo nella pelle, allargando il brufolo e prolungando il processo di guarigione. Inoltre, batteri e l'olio possono diffondersi e portare a più acne in altre zone. Infine, scoppiare un brufolo può causare una cicatrice permanente, mentre l'infiammazione è solo temporanea.
Sono allergico a qualcosa?
Anche se non sviluppi sintomi tipici dell'allergia, come starnuti o prurito, è possibile che la tua pelle reagisca a determinati alimenti. Ciò accade attraverso l'intestino, che lascia passare molecole più grandi, a cui il sistema immunitario reagisce e provoca un processo di infiammazione. Il consumo di latticini e cibi ad alto indice glicemico sono legati al peggioramento dell'acne in alcune persone, ma anche altri alimenti possono causare infiammazione. Per scoprire se sei sensibile a determinati alimenti, prova a limitare quelli che sospetti per 6 settimane (il tempo che la tua pelle impiega per guarire). Se non vedi alcun miglioramento dopo questo periodo, è probabile che la causa sia un´altra.
Anche la sensibilità ad alcuni prodotti per la cura della pelle come creme, saponi o trucco può causare l'acne. (5,6,7)
Dipende da cosa mangio?
La pelle è influenzata da ciò che mangi, poiché esiste una connessione tra i batteri nell'intestino e la cute. Tuttavia, questo può variare da persona a persona. La ricerca mostra che una dieta ricca di alimenti ad alto indice glicemico e latticini può peggiorare l'acne in alcune persone. Raccomandiamo una dieta equilibrata con abbastanza fibre (prodotti integrali) e di evitare cibi ultra-lavorati e limitare il consumo di latticini. Poiché ogni corpo reagisce in modo diverso, non è garantito che questi cambiamenti nella dieta curino l'acne. Se l'acne persiste, contattare il medico di famiglia o il dermatologo. (8,9,10)
Che dire dell'acne e del cioccolato?
Forse la gente ti ha detto che mangiare cioccolato peggiorerà la tua acne; questo non è del tutto vero. Gli alimenti ad alto indice glicemico come il cioccolato sono generalmente peggiori per la salute generale e quindi anche per la cute. Poiché lo zucchero viene spesso aggiunto al cioccolato, ciò può effettivamente causare un aumento dell'acne. Tuttavia, come con tutte le diete, l'equilibrio è la chiave. Finché mangi una dieta equilibrata con la maggior parte dei cibi a basso indice glicemico e non ultra-lavorati, un pezzo di cioccolato ogni tanto non farà male. Un'alternativa più sana può essere il cioccolato fondente. Presta attenzione alla percentuale di cacao nel cioccolato (70% o superiore): maggiore è questa percentuale, meno zucchero viene aggiunto. Quantità eccessive di zucchero in generale possono effettivamente peggiorare l'acne. (9)
Lavare spesso aiuta?
Il lavaggio ossessivo può peggiorare l'acne, poiché danneggia la barriera protettiva naturale della pelle. Dal momento che un brufolo si forma all'interno del follicolo del sebo, non puoi rimuoverlo lavando il viso con sapone.
Lavarsi il viso 1-2 volte al giorno (al mattino e / o alla sera) è sufficiente. È molto importante purificare il viso a fine giornata, soprattutto quando ci si trucca. Anche il prodotto che usi per il lavaggio, è importante. Alcuni ingredienti possono seccare e / o irritare la pelle.
Si consiglia di usare un detergente delicato con acido salicilico al 2% (da evitare se si sta già facendo una terapia esfoliante). L'acido salicilico è l'unico ingrediente che raggiunge i follicoli e può eliminare l'acne. Assicurati di usare crema solare (almeno SPF30) durante il giorno, poiché l'acido salicilico rende la pelle più sensibile al sole. (5)
Uso solo cosmetici naturali, perché la mia acne non migliora?
Molte marche affermano che il loro prodotto naturale faccia miracoli per curare l'acne. Tuttavia, proprio come qualsiasi altro prodotto, può ostruire i pori e causare l'acne. È anche possibile avere un'allergia agli ingredienti naturali. Alcuni ingredienti che non sono "naturali" possono aiutarti a schiarire molto la pelle senza danneggiarla. Perciò: il naturale non è sempre meglio. Quando si tratta di cura della pelle, è importante che i prodotti che utilizzi siano basati sul tuo tipo di pelle. Poiché l'acne si presenta in modi diversi da persona a persona, è importante utilizzare un prodotto che tratta il tuo tipo specifico di acne e non ha additivi inutili. (11)
Indossare trucco / fondotinta peggiora la mia acne?
Indossare il trucco, e in particolare le fondotinte o le ciprie, può effettivamente causare o peggiorare l'acne. I prodotti possono ostruire i pori, il che aiuta i batteri dell'acne a crescere. Se scegli ancora di truccarti, è importante scegliere una base non comedogena. Inoltre è molto importante pulire a fondo il viso dopo una giornata trascorsa con il trucco. Puoi farlo usando un'acqua micellare e successivamente usando un detergente delicato con acido salicilico al 2% per ridurre l'acne. (5,7)
Perché le creme per l'acne della farmacia non migliorano la situazione?
Perché ci sono diversi tipi di acne, ogni tipo ha bisogno di un trattamento diverso. Per trovare il prodotto giusto, è meglio lasciare che un dermatologo ti visiti per diagnosticare il tipo di acne che hai e informarti su quale trattamento o crema sarebbe meglio usare.
In che modo la pillola anticoncezionale aiuta la mia acne?
I fattori che causano l'acne sono influenzati dagli ormoni, principalmente dagli ormoni estrogeni e testosterone (androgeni). In breve; il testosterone tende a peggiorare l'acne, gli estrogeni la migliorano. Qualsiasi cambiamento di ormoni nel corpo, può quindi portare a un peggioramento dell'acne. Durante la pubertà, un aumento del testosterone allarga i follicoli del sebo, il che li fa produrre più sebo e può provocare più acne. Ma anche dopo la pubertà, diminuzioni di estrogeni e aumenti di testosterone sono normali e possono peggiorare l'acne a qualsiasi età.
Per trattare questo fattore ormonale, alcuni tipi di pillola anticoncezionale vengono utilizzati nel trattamento dell'acne. Gli ormoni in queste pillole riducono la quantità di testosterone nel corpo e quindi riducono l'acne. (12)
La pillola anticoncezionale è un buon modo per curare l'acne?
La pillola anticoncezionale può effettivamente essere efficace per curare l'acne nelle donne, quando sono in età fertile e desiderano anche usare la contraccezione. Alcuni tipi di pillola anticoncezionale sono più efficaci di altri. Per il trattamento dell'acne, viene spesso utilizzata in combinazione con una crema o con pillole antibiotiche.
Tuttavia, per alcuni tipi di acne (lieve), è meglio iniziare solo con una crema o un antibiotico senza terapia ormonale. Un trattamento ormonale dell'acne non è la soluzione per tutti, un medico sarà in grado di consigliarti al riguardo. (13,14)
Le creme per l'acne mi rendono allergico, cosa posso fare?
Alcuni ingredienti nelle creme per l'acne, come il perossido di benzoile e l'acido salicilico, possono irritare la pelle causando arrossamenti, bruciore, prurito e secchezza. È probabile che ciò accada quando la barriera protettiva naturale della pelle è danneggiata. Per prevenire questo danno, è importante non lavare la pelle troppo spesso e non usare troppi prodotti diversi contemporaneamente. Se tendi ad avere la pelle sensibile, può essere difficile trovare una crema per l'acne adatta a te. Un dermatologo può aiutarti a trovare un trattamento efficace. (15)
Come posso prevenire le cicatrici da acne?
La cosa migliore che puoi fare per prevenire le cicatrici, è non scoppiare o graffiare eventuali brufoli. Quando fai scoppiare un brufolo, c'è una grande possibilità che alcuni residui rimangano nel follicolo e la guarigione richiederà più tempo. Se lasci che la pelle si prenda cura del brufolo da sola, c'è una maggiore possibilità che guarisca velocemente senza cicatrici. Oltre a ciò, puoi pulire la pelle 1-2 volte al giorno con un detergente acido salicilico per prevenire eventuali nuovi brufoli. (5)
Come posso rendere le cicatrici meno visibili?
A seconda del tipo e della dimensione delle cicatrici, ci sono diverse opzioni per renderle meno visibili.
Quando hai cicatrici rosse e piatte, di solito scompaiono nel tempo. Esfolianti chimici o determinati prodotti possono aiutare ad accelerare il recupero. Per mascherare le cicatrici puoi usare per il trucco ma è importante rimuoverlo a fine giornata per prevenire la formazione di nuovi brufoli.
Le cicatrici di colore più scuro possono sbiadire un po' nel tempo ma per trattarle sono necessari trattamenti laser, peeling chimici o retinoidi (crema).
Per le cicatrici atrofiche (fossette) è più difficile coprirle con il trucco. A seconda delle dimensioni, ci sono alcuni trattamenti possibili, come laser, peeling chimico, filler o escissione.
Se scegli di sottoporsi a un trattamento per ridurre la visibilità delle cicatrici da acne, un dermatologo sarà in grado di consigliarti su quale trattamento funzionerà meglio per te. (16,17)
Cosa posso fare per l'acne su schiena, spalle e petto?
Il motivo per cui hai l'acne in queste zone è perché, insieme al viso, hanno più follicoli rispetto rispetto al resto del corpo. Pertanto questa zona è più sensibile all'attrito (ad esempio uno zaino) o ai prodotti per capelli (come un olio ma anche un balsamo) che ostruiscono i follicoli.
Per le spalle e il torace è possibile utilizzare i prodotti per il viso (detergente acido salicilico al 2% sotto la doccia, per esempio Rev Acnosal mousse), ma il trattamento per la schiena può essere più difficile in quanto è difficile da raggiungere. Noi raccomandiamo preparati spray in quanto facili da usare. (5)
I lettini abbronzanti fanno bene all'acne?
Alcune persone potrebbero dire che i lettini abbronzanti aiutano a chiarire l´acne. Questo non è del tutto vero: la pelle più scura rende meno visibile la comparsa di macchie rosse. Anche se questa può sembrare una buona soluzione, consigliamo di non usare lettini abbronzanti. C'è un'alta probabilità di sviluppare il cancro della pelle, proprio come con il sole normale (usare sempre crema solare quando esposti al sole). Esistono molti trattamenti alternativi che possono aiutarti a gestire l'acne. (18)
Cosa posso fare per migliorare la mia acne?
Per gestire l'acne, è importante seguire alcuni semplici passaggi: lava il viso 1-2 volte al giorno con un detergente con acido salicilico al 2% delicato, usa una crema idratante senza alcool / profumo e usa prodotti non comedogeni. Cerca di toccarti il viso il meno possibile e non graffiare o far scoppiare i brufoli. Per vedere se hai intolleranze alimentari che causano o aggravano l'acne, puoi provare a limitare i latticini e mangiare cibi a basso indice glicemico. Una dieta sana ed equilibrata con frutta e verdura sufficienti può contribuire alla salute della pelle e della persona in generale. Se la tua acne persiste o se hai ulteriori domande, contatta il tuo dermatologo. (5,6)
Referenze
(1) Degitz, K., Placzek, M., Borelli, C., & Plewig, G. (2007). Pathophysiology of acne. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft. 5(4), 316-323.
(2) Baumann, L. (2009). The Baumann Skin-Type Indicator: A Novel Approach to Understanding Skin Type. In A.O. Barel., M. Paye, & H.I., Maibach (Ed.), Handbook of Cosmetic Science and Technology (3rd ed.) (pp. 29-40). New York, United States: Informa Healthcare.
(3) Bagatin, E., Freitas, T.H.P., Rivitti-Machado, M.C., Machado, M.C.R., Ribeiro, B.M., Nunes, S., & Rocha, M.A.D.D. (2019). Adult female acne: a guide to clinical practice. Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia. 94(1), 62-75.
(4) Chlebus, E., & Chlebus, M. (2017). Factors affecting the course and severity of adult acne. Observational cohort study. Journal of Dermatological Treatment. 28(8), 737-744.
(5) Baumann, L., & Keri, J. (2009). Acne (Type 1 Sensitive Skin). In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 121-127). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(6) Bowe, W.P., & Logan, A.C. (2011). Acne vulgaris, probiotics and the gut-brain-skin axis - back to the future? Gut Pathogens. 3(1), 1-11.
(7) Singh, S., Mann, B.K., & Tiwary, N.K. (2013). Acne cosmetica revisited: a case control study shows a dose dependent inverse association between overall cosmetic use and post-adolescent acne. Dermatology. 226(4), 337-341.
(8) Matsui, M.S. (2019). Update on diet and acne. Cutis. 104(1), 11-13.
(9) Baumann, L. (2009). Nutrition and the Skin In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 46-66). NewYork, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(10) Perricone, N. (2003). The Acne Prescription: The Perricone Program for Clear and Healthy Skin At Every Age. New York, United States: Harper Collins.
(11) Weisberg, E., & Baumann, L. (2009). Cosmetic and Drug Regulation. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 241-244). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(12) Zaulyanov-Scanlan, L. (2009). Hormones and Aging Skin. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 29-33). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(13) Katsambas, A.D., & Dessiniori, C. (2010). Hormonal therapy for acne: why not as first line therapy? Facts and Controversies. Clinics in Dermatology. 28(1), 17-23.
(14) Zouboulis, C.C., & Rabe, T. (2010). Hormonal antiandrogens in acne treatment. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft. 8, 60-74.
(15) Baumann, L. (2009). Sensitive Skin. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 94-97). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(16) Obagi, S., & Casey, A. (2009). Facial Scar Revision. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 227-234). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(17) Baumann, L., & Saghari, S. (2009). Skin Pigmentation and Pigmentation Disorders. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 98-108). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(18) Radack, K.P., Farhangian, M.E., Anderson, K.L., & Feldman, S. (2015). A review of the use of tanning beds as a dermatological treatment. Dermatology and Therapy. 5, 37-51.
Why do I have acne?
Acne is caused by a combination of four factors; higher production of sebum, clogged pores, the presence of a specific bacteria and inflammation. The production of sebum is influenced by hormones. Therefore acne often exists during puberty, but can occur in any age, especially in women since they have more hormonal changes during their lifetime. Not every person gets the same amount of acne because people’s sebum follicles react in different ways to the changes in the body.
It is known that acne runs in families. When (one of) your parents had acne, it’s more likely that you have it as well. Also stress and wrong skin care can worsen acne.
Often the specific cause of acne is unclear and difficult to determine. However, with the right treatment it can be possible to manage the acne. (1,2)
I am not in puberty anymore, how come I still have acne?
During puberty, hormones make you skin produce more sebum, which causes acne. But also in later ages, hormonal imbalances can cause more acne. This happens a lot in women, for example before menstruation or during pregnancy, but also other factors can contribute. Stress, sensitive skin, skin-care products, smoking, diet, certain medication and endocrine diseases are only a few examples of what can can worsen acne at any age. (3,4)
Does popping pimples make it worse?
In most cases, this is indeed true. Some professionals can indeed clear (‘pop’) some types of pimples, but doing it yourself will almost always make it worse than it was before. By having acne, your body is responding to blocked pores and bacteria, the bump means your body is trying to heal the skin.
Instead of making progress, you will force bacteria and oil even deeper into the skin, making the pimple larger and the healing process longer. Also, the bacteria and oil can spread and lead to more acne on another site. Lastly, popping will likely cause a permanent scar, while a pimple is only temporary.
Am I allergic to something?
This is a possibility. Even if you don’t develop typical allergy symptoms like sneezing or itchiness, it can be that your skin reacts to certain foods. This happens through the intestines, that lets through bigger molecules that the immune system reacts to and causes an inflammation process. What type foods these are, can be different for each person. Dairy consumption and high glycemic foods are linked to worsening acne in some people, but also other foods can cause inflammation. To find out if you are sensitive to any foods, try to limit the foods that you suspect for 6 weeks. This is the time your skin needs to heal. If you see no improvement after this period, it is likely that your acne has another cause.
Also a sensitivity to certain skin-care products like creams, soaps or makeup can cause acne. (5,6,7)
Does it depend on what I eat?
What you eat can have an influence on your skin, since there is a connection between bacteria in the gut and the skin. However, this can vary from person to person. Research shows that a high glycemic diet and dairy can worsen acne in some people. We recommend a balanced diet with enough fiber (wholegrain products) and to avoid highly processed foods, and to limit dairy consumption. Since every body reacts differently, it is not guaranteed that these dietary changes will cure acne. If the acne persists, contact the GP or dermatologist. (8,9,10)
What about acne and chocolate?
Maybe people told you that eating chocolate will make your acne worse. However, this is not entirely true. High glycemic foods like chocolate are in general worse for your overall health and therefore also for your skin. Since sugar is often added to chocolate, this can indeed cause an increase of acne. However, like with all diets, balance is key. As long as you eat a balanced diet with a majority of low glycemic and unprocessed foods, a piece of chocolate every now and then will not hurt. A healthier alternative can be dark chocolate. Pay attention to the percentage of cacao in the chocolate (70% or higher); the higher this percentage, the less sugar is added. Excessive amounts of chocolate (or sugar in general) can indeed worsen acne. (9)
Does washing often help?
Obsessive washing can make acne worse, because it damages the natural protective barrier of the skin. Since a pimple forms inside of the sebum follicle, you are not able to remove that by washing your face with soap.
Washing your face 1-2 times a day (in the morning and/or evening) is enough. It is very important to cleanse your face at the end of the day, especially when you wear makeup. The product you use to cleanse, is also important. Some ingredients can dry out and/or irritate the skin.
Washing with a mild 2% salicylic acid cleanser is recommended. Salicylic acid is the only ingredient that does reach inside of the follicles and can clear up acne. Make sure to use at least SPF30 during the day, since the salicylic acid makes your skin more sensitive for the sun. (5)
I use only natural cosmetics, why does my acne not get better?
A lot of brands claim that their natural product does wonders to heal your acne. However, just as any other product, they can clog your pores and cause acne. It is also possible to have an allergy to natural ingredients. And some ingredients that are not ‘natural’, can help clear up your skin a lot without damaging it. Therefore; natural is not always better. When it comes to skincare, it is important that the products you use, are based on your skin type. Since acne occurs in different ways from person to person, it is important to use a product that treats your specific type of acne and does not have unnecessary additives. (11)
Does wearing makeup/foundation make my acne worse?
Wearing makeup, and especially foundation or face powders, can indeed cause or worsen acne. The products can clog pores, which helps acne-bacteria to grow. If you still choose to wear makeup, it is important to choose a foundation that is non-comedogenic. Besides that it is very important to cleanse the face thoroughly after a day of wearing makeup. You can do this by using a micellar water and afterwards using a mild cleanser with 2% salicylic acid to reduce the acne. (5,7)
Why do acne creams from the drugstore not make it better?
Since there are different types of acne, every type needs a different method to treat it. In order to find the right product, it is best to let a dermatologist look at your acne. He can diagnose what kind of acne you have, and inform you about what treatment or cream would be best to treat your acne.
How does the birth control pill help my acne?
The factors that cause acne are influenced by hormones, mainly by the hormones estrogen and testosterone (androgens). In short; testosterone tends to make acne worse, estrogen makes it better. Any change of hormones in the body, can therefore lead to worsening of acne. During puberty, an increase of testosterone makes the sebum follicles larger, which makes them produce more sebum and can result in more acne. But also after puberty decreases of estrogen and increases of testosterone are normal, and can worsen acne at any age.
To treat this hormonal factor, some types of birth control pill are used in the treatment of acne. The hormones in these pills reduce the amount of testosterone in the body, and therefore reduce acne. (12)
Is the birth control pill a good way to treat acne?
The birth control pill can indeed be effective to treat acne in women, when they’re in fertile age and also have a wish of using contraception. Some types of birth control pill are more effective than others. For the treatment of acne, it is often used in combination with a cream or antibiotic pills.
However, for some types of (mild) acne, it is better to start with only a cream or antibiotic without hormonal therapy. This might be enough to treat the acne. Also a hormonal treatment of acne will not be the solution for everyone. A GP will be able to advise you on this. (13,14)
Acne creams make me allergic, what can I do?
Certain ingredients in acne creams like benzoyl peroxide and salicylic acid, can irritate the skin. It can cause redness, burning, itchiness and flakes. This is likely to happen when the natural protective barrier of the skin is damaged. To prevent this damage, it is important to not wash the skin too often and to not use too many different products at the same time. If you tend to have sensitive skin, it can be difficult to find an acne cream that works for you. A dermatologist can help you with finding an effective treatment. (15)
How can I prevent acne scars?
The best thing you can do to prevent scars, is to not pop or scratch any pimples. When you pop a pimple, there is a big chance that some residue will stay behind, and the inflammation process will take longer. If you let the skin take care of the pimple by itself, there is a bigger chance that it will heal fast without scars. Besides that, you can cleanse your skin 1-2 times a day with a salicylic acid cleanser to prevent any new pimples. (5)
How can I make the scars less visible?
Depending on the type and size of the scars, there are different options to make acne scars less visible.
When you have red, flat scars, they usually disappear over time. Chemical peelings or certain products can help speed up the recovery. To mask the scars you can use makeup, it is important to remove this at the end of the day to prevent the formation of new pimples. Darker colored scars can fade a bit over time and can be covered up with makeup. To treat them, laser treatment, chemical peels or retinoids (cream) are possible.
For atrophic scars (dimples) it is more difficult to cover them up with makeup. Depending on the size, there are some treatments possible, like laser, chemical peeling, fillers or excision.
If you choose to have treatment to reduce the visibility of acne scars, a dermatologist will be able to advise you on which treatment will work best for you. (16,17)
What can I do about acne on my back, shoulders and chest?
The reason you have acne on your back, shoulders and chest, is because there are a lot more sebum follicles on those parts of your body and your face, compared to the rest of your body. Therefore this area is more sensitive to friction (from for example a backpack) or hair products (like an oil but even conditioner) that clog the follicles.
For your shoulders and chest you can use the same skincare as for your face (2% salicylic acid cleanser in the shower), but treatment for the back can be more difficult as it is hard to reach. We recommend spray formulations as they are easy to use.(5)
Are tanning beds good for acne?
Some people might say that tanning beds will help clear up your acne. This is not entirely true; the darker skin just makes the appearance of red spots less visible. Even if this may seem like a good solution, we recommend to not use tanning beds. There is a high chance of developing skin cancer, just like with the normal sun. Always use at least SPF30 when you spend time outside to prevent skin cancer. There are plenty of alternative treatments that can help you manage the acne. (18)
What can I do to clear up my acne?
To manage the acne, it is important to follow a few simple steps. Wash your face 1-2 times a day with a mild 2% salicylic acid cleanser, use a hydrating cream without alcohol/perfume and use non-comedogenic products. Try to touch your face as little as necessary, and don’t scratch or pop the pimples. To see if you have any food intolerances that cause or aggravate the acne, you can try to limit diary and eat mostly low glycemic foods. A healthy, balanced diet with enough vegetables and fruits can help contribute to your health and skin. If your acne persists or if you have any questions, contact your dermatologist. (5,6)
References
(1) Degitz, K., Placzek, M., Borelli, C., & Plewig, G. (2007). Pathophysiology of acne. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft. 5(4), 316-323.
(2) Baumann, L. (2009). The Baumann Skin-Type Indicator: A Novel Approach to Understanding Skin Type. In A.O. Barel., M. Paye, & H.I., Maibach (Ed.), Handbook of Cosmetic Science and Technology (3rd ed.) (pp. 29-40). New York, United States: Informa Healthcare.
(3) Bagatin, E., Freitas, T.H.P., Rivitti-Machado, M.C., Machado, M.C.R., Ribeiro, B.M., Nunes, S., & Rocha, M.A.D.D. (2019). Adult female acne: a guide to clinical practice. Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia. 94(1), 62-75.
(4) Chlebus, E., & Chlebus, M. (2017). Factors affecting the course and severity of adult acne. Observational cohort study. Journal of Dermatological Treatment. 28(8), 737-744.
(5) Baumann, L., & Keri, J. (2009). Acne (Type 1 Sensitive Skin). In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 121-127). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(6) Bowe, W.P., & Logan, A.C. (2011). Acne vulgaris, probiotics and the gut-brain-skin axis - back to the future? Gut Pathogens. 3(1), 1-11.
(7) Singh, S., Mann, B.K., & Tiwary, N.K. (2013). Acne cosmetica revisited: a case control study shows a dose dependent inverse association between overall cosmetic use and post-adolescent acne. Dermatology. 226(4), 337-341.
(8) Matsui, M.S. (2019). Update on diet and acne. Cutis. 104(1), 11-13.
(9) Baumann, L. (2009). Nutrition and the Skin In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 46-66). NewYork, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(10) Perricone, N. (2003). The Acne Prescription: The Perricone Program for Clear and Healthy Skin At Every Age. New York, United States: Harper Collins.
(11) Weisberg, E., & Baumann, L. (2009). Cosmetic and Drug Regulation. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 241-244). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(12) Zaulyanov-Scanlan, L. (2009). Hormones and Aging Skin. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 29-33). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(13) Katsambas, A.D., & Dessiniori, C. (2010). Hormonal therapy for acne: why not as first line therapy? Facts and Controversies. Clinics in Dermatology. 28(1), 17-23.
(14) Zouboulis, C.C., & Rabe, T. (2010). Hormonal antiandrogens in acne treatment. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft. 8, 60-74.
(15) Baumann, L. (2009). Sensitive Skin. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 94-97). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(16) Obagi, S., & Casey, A. (2009). Facial Scar Revision. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 227-234). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(17) Baumann, L., & Saghari, S. (2009). Skin Pigmentation and Pigmentation Disorders. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 98-108). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(18) Radack, K.P., Farhangian, M.E., Anderson, K.L., & Feldman, S. (2015). A review of the use of tanning beds as a dermatological treatment. Dermatology and Therapy. 5, 37-51.
Invecchiamento della pelle
curato da Anissa Westenberg
Quali sono le cause dell'invecchiamento cutaneo?
L'invecchiamento cutaneo è causato da due processi: invecchiamento intrinseco ed estrinseco. L'invecchiamento intrinseco è genetico ed è l'invecchiamento naturale del corpo quindi possiamo influenzarlo solo in piccola parte. L'invecchiamento estrinseco è causato da fattori esterni, come lo stile di vita di una persona. Questa è la parte che possiamo influenzare maggiormente e quindi possiamo rallentare il processo dell’invecchiamento e apparire giovani più a lungo.
Parti del corpo che sono esposte al sole, come il viso, il torace, gli avambracci e le mani, di solito mostrano la maggior parte dei segni dell'invecchiamento della pelle (come macchie scure e rughe). Queste parti soffrono maggiormente a causa di un importante fattore estrinseco: il sole. Il sole è responsabile dell'80% dell'invecchiamento cutaneo estrinseco. (1,2)
Come posso prevenire l'invecchiamento della pelle?
Dato che il sole è un grande fattore estrinseco nell'invecchiamento cutaneo, è molto importante proteggere la pelle dal sole. Il modo migliore per farlo è evitare la luce solare diretta il più possibile, specialmente dalle 10:00 alle 16:00. Si consiglia inoltre di applicare una crema solare di almeno SPF30 ogni mattina e di ripetere l'operazione durante il giorno quando la pelle è esposta al sole. Anche fumare contribuisce all'invecchiamento cutaneo e in particolare alla formazione di rughe. È dimostrato che i pazienti che fumano, avranno meno risultati dai trattamenti anti-invecchiamento rispetto alle persone che non fumano. Pertanto si consiglia di smettere di fumare. Oltre a ciò, una cattiva alimentazione e il consumo di alcolici aggraveranno l'invecchiamento della pelle. Assicurati di seguire una dieta equilibrata con: Più frutta, verdura e prodotti integrali.
Meno cibo ultra processato, zuccheri semplici (cibi con un alto contenuto di zuccheri; attenzione ai prodotti con zucchero aggiunto quali prodotti da forno e alcuni cereali) e consumo di alcolici ridotto. (2,3,4)
Le creme anti-età che posso acquistare in farmacia funzionano?
Al giorno d'oggi ci sono molti prodotti anti-invecchiamento venduti in farmacia. Ma come fare a sapere se funzionano? L'ingrediente più importante in una crema anti-invecchiamento dovrebbe essere la protezione solare. La maggior parte delle creme da giorno hanno un SPF (fattore di protezione solare), ma spesso è troppo basso. Per proteggere la pelle dal sole, è necessario almeno SPF30. Devi riapplicare la protezione solare durante la giornata se sei all'esterno, perché il SPF funzionerà con il fattore massimo solo per 2 ore.
Le creme anti invecchiamento hanno spesso ingredienti attivi: ingredienti speciali che combatteranno i segni dell'invecchiamento. A volte la concentrazione di questi ingredienti efficaci è così bassa che non fanno molto per la tua pelle.
La maggior parte delle creme sono idratanti, questo aiuterà a rendere la cute più giovane. Ma spesso viene aggiunto il profumo e, a seconda della quantità, questo ingrediente secca il derma e aggrava la comparsa delle rughe.
È difficile dire se una crema è efficace o meno, ma tieni presente che le creme spesso non sono così efficaci come sostengono nelle pubblicità. Non avere grandi aspettative. Le creme possono aiutare a migliorare le linee sottili, la secchezza e la consistenza della pelle. Esse hanno un'efficacia preventiva e contribuiscono a ritardare l’invecchiamento del derma. I segni più pronunciati dell'invecchiamento tuttavia richiedono un trattamento dermatologico per migliorare.
Come posso trovare una buona crema anti età?
Per trovare una crema anti età che funzioni per te, è importante sapere che tipo di pelle hai. Se hai la pelle sensibile, avrai bisogno di prodotti che abbiano meno rischio di irritarla.
La crema idratante (ristrutturante) è la prima cosa che vuoi cercare. Questa crema ristrutturerà i normali componenti della pelle che diminuiscono con l’età rendendo meno visibili le rughe sottili. Il componente più importante in una crema che usi per il giorno è la protezione solare, in quanto ciò impedisce (ulteriori) segni di invecchiamento. Cerca una crema che offra almeno SPF30. Una crema idratante per la sera invece, non ha bisogno di SPF.
La crema idratante può avere determinati ingredienti attivi (ingredienti che agiscono contro i segni dell'invecchiamento). Il retinolo è molto efficace, tuttavia questo ingrediente dovrebbe essere evitato se si ha la pelle sensibile. Gli antiossidanti come la vitamina C sono gli ingredienti che vuoi cercare quando vuoi prevenire le rughe.
Non è sempre vero che il prodotto più costoso funzionerà al meglio; i prodotti efficaci sono disponibili in tutti i prezzi. (5)
Cosa sono esattamente gli antiossidanti, il collagene, il Q10, il retinolo e l'acido ialuronico?
Alcuni ingredienti sono spesso utilizzati nei prodotti anti-invecchiamento. Ma cosa sono esattamente e come funzionano?
Gli antiossidanti sono sostanze che possono prevenire o rallentare i danni causati dai radicali liberi alle cellule. I radicali liberi sono molecole che il corpo produce come reazione a fattori ambientali come fumare, la luce solare e l'inquinamento atmosferico. Gli antiossidanti si trovano spesso in frutta e verdura. La maggior parte degli antiossidanti previene l'invecchiamento cutaneo, ma non lo tratta. L'unico antiossidante che può curare le rughe è la vitamina C.
Il collagene è una proteina che fornisce forza e struttura alla pelle e si trova naturalmente nel corpo. È scomposto nel tempo dai radicali liberi. Questo processo provoca rughe. Il collagene può essere aggiunto alle creme per idratare la pelle e mantenerla elastica, rendendo le rughe meno pronunciate. Tuttavia, il collagene in una crema non può annullare la perdita naturale di collagene della pelle e far scomparire le rughe.
Il Q10 è un tipo di antiossidante che si trova naturalmente nel corpo, ma diminuisce con l'età. Si può trovare in pesci e crostacei. Se usato in una crema, può penetrare nella pelle e rendere le rughe meno profonde e prevenire altri segni dell'invecchiamento, come la pigmentazione.
Il retinolo è un tipo di vitamina A. È un ingrediente che accelera il rinnovamento della pelle e riduce i danni al collagene. Di conseguenza riduce la comparsa di linee sottili, rughe e macchie dell'età. Tuttavia, questo prodotto non funziona per tutti. Alcune persone tendono a reagire in modo allergico quando usano una crema con retinolo.
L'acido ialuronico è una sostanza che si trova naturalmente nel corpo e si decompone nel tempo. Se presente nella crema, l'acido penetra attraverso la pelle e si attacca all'acqua per fornire luminosità e pienezza alla pelle, riducendo quindi la comparsa di rughe. (6,7,8)
Dovrei prendere integratori?
Ci sono alcuni integratori sul mercato che vengono pubblicizzati come anti-invecchiamento. Ma quali integratori sono buoni e di quali hai bisogno? Si raccomanda una dieta sana ed equilibrata con abbastanza vitamine da frutta e verdura. Questi ti daranno la maggior parte, se non tutte le vitamine di cui hai bisogno. Non hai "bisogno" di integratori, tuttavia, a volte possono aiutare con alcuni processi nel corpo. In base ai nutrienti forniti dalla dieta, puoi decidere di assumere determinati integratori.
Al mattino si consigliano 200 mg di coQ10 per ridurre le rughe in età avanzata. Si può trovare anche in pesci e crostacei.
Gli integratori di Omega 3 possono aiutare a idratare la pelle e ridurre al minimo le linee. Questo acido grasso salutare non è prodotto dal corpo, quindi deve essere introdotto attraverso alimenti come pesce, noci e semi di lino.
La vitamina C aumenta la produzione di collagene e si trova in agrumi, pomodori e peperoni. (7,9)
A che età dovrei iniziare a usare prodotti anti-invecchiamento?
La prevenzione è la cosa migliore che puoi fare quando si tratta di trattamenti anti-invecchiamento. Poiché il sole è il fattore più importante che contribuisce all'invecchiamento della pelle, è meglio iniziare il più presto possibile a proteggere la pelle dai raggi solari. Ciò non solo previene la (ulteriore) formazione di rughe e macchie, ma previene anche il cancro della pelle. (5)
Quali trattamenti ci sono per trattare l'invecchiamento della pelle?
Esistono molti modi per trattare i segni dell'invecchiamento. A seconda del tipo di segni e della gravità, è possibile trovare un trattamento per quasi ogni problema. Un dermatologo sarà in grado di consigliarti sulle opzioni che si adattano alla tua pelle e ai tuoi desideri. Questi sono i trattamenti anti-età che eseguiamo a DermoVicenza:
Il laser CO2 può essere usato per rimuovere le verruche seborroiche e per curare le rughe. Per il massimo effetto nel trattamento delle rughe, un peeling TCA può successivamente essere applicato sull'area.
Il laser Q-switch Nd:YAG può essere usato per trattare le macchie pigmentate dell'età e per la biostimolazione; un tipo di peeling che tratta le rughe.
Iniezioni di botulino e acido ialuronico per il trattamento delle rughe.
La radiofrequenza ad aghi trova indicazione soprattutto nel trattamento della pelle rilassata del collo e delle braccia.
Come devo prendermi cura della mia pelle ogni giorno?
Puoi iniziare la giornata usando un detergente delicato per pulire il viso, seguito da una creme da giorno con almeno SPF30 per proteggere la pelle dal sole. In seguito se vuoi puoi applicare il trucco. Applica crema solare durante il giorno e non dimenticare di applicarla anche sul petto, sugli avambracci e sulle mani, poiché questi sono spesso esposti al sole.
La sera, puoi usare un'acqua micellare per togliere il trucco e usare un detergente delicato per rimuovere lo sporco in eccesso per poi finire con una crema ristrutturante. (5)
Ho delle macchie sulla pelle, cosa posso fare al riguardo?
Esistono alcuni tipi di punti che si sviluppano o aumentano in età avanzata. Molti di questi possono essere trattati molto facilmente.
Queste macchie rosse sono chiamate angiomi rubino. Sembrano nei rossi a causa della raccolta di vasi sanguigni al loro interno. Si possono trovare principalmente sul tronco, ma anche su altre regioni del corpo. Non andranno via da soli. Gli angiomi rubino non sono motivo di preoccupazione finché non sanguinano o cambiano in dimensioni, forma o colore. Possono essere trattati con un laser vascolare a Diodo o elettrocoagulazione.
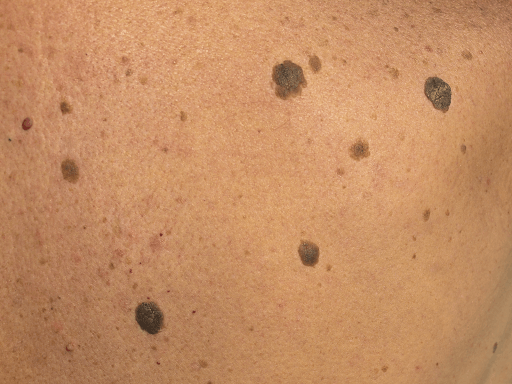
Le verruche senili, note anche come verruche seborroiche, sono macchie ruvide e scure. Sono solitamente in rilievo sulla pelle e aumentano con l'età. Possono svilupparsi in qualsiasi parte del corpo, ma si trovano principalmente sulla testa e sul tronco. Possono essere facilmente rimossi con elettrocoagulazione, laser CO2, crioterapia o escissione.
Le macchie solari, chiamate anche lentigo solaris/senilis, sono macchie che si sviluppano in aree che sono state spesso esposte al sole come: mani, ascelle, viso, petto e spalle. Possono essere trattati con il laser Q-switch Nd:YAG, che si concentra sul pigmento più scuro nelle macchie.
I porri (fibroma molle) sono spesso visti sul collo e sulle ascelle, ma possono svilupparsi anche in altre aree. Di solito si formano a causa di attrito e/o irritazione della pelle. Possono essere facilmente rimossi con elettrocoagulazione o una semplice escissione.
What causes skin aging?
Skin aging is caused by two processes: intrinsic and extrinsic aging. The intrinsic aging is the genetic background and natural aging of the body, therefore it is out of our control and we cannot prevent it. Extrinsic aging is caused by factors from the outside, like a person's lifestyle. This is the part that we can influence and therefore we can prevent skin aging partially.
Parts of the body that are exposed to the sun, like the face, chest, forearms and hands usually show most signs of skin aging (like dark spots and wrinkles). These parts suffer the most from one important extrinsic factor; the sun. The sun is responsible for 80% of extrinsic skin aging.
How can I prevent skin aging?
Because sun exposure is a big extrinsic factor in skin aging, it is very important to protect your skin from the sun. The best way to do this, is to avoid direct sunlight as much as possible, especially in between 10AM and 4 PM. Besides that it is recommended to apply a sunscreen of at least SPF30 every morning, and to repeat it during the day when the skin is exposed to the sun.
Smoking also contributes to skin aging, and to the formation of wrinkles in particular. It is proven that patients who smoke, will have less results from anti-aging treatments than people who don’t smoke. Therefore it is recommended to quit smoking.
Besides that, poor nutrition and drinking alcohol will aggravate skin aging. Make sure to eat a balanced diet with less processed foods and enough vegetables and fruits, and limit alcohol consumption.
Do anti-aging creams that I can buy at the drugstore work?
There are a lot of anti-aging products being sold at the drugstore nowadays. But how do you know if they work? The most important ingredient in an anti-aging cream should be sunscreen. Most day creams do have an SPF, but often the SPF is too low. To protect your skin from the sun, you will need at least SPF30. You have to reapply sunscreen during the day when you’re outside, because the SPF will only work with the maximum factor for 2 hours.
Anti aging creams often have active ingredients; special ingredients that will combat the signs of aging. Sometimes the concentration of these effective ingredients is so low, that they don’t do much for your skin.
Most creams are hydrating, this will help make the skin look younger. But often perfume is added, and depending on the amount, this ingredient dries out the skin and aggravates the appearance of wrinkles.
It is difficult to say if a cream is effective or not, but keep in mind that creams are often not as effective as they claim to be in commercials. Don’t have high expectations. Creams can help improving fine lines, dryness and the texture of the skin, but more pronounced signs of aging will need dermatological treatment to improve.
How can I find a good anti-aging cream?
To find an anti-aging cream that will work for you, it is important to know what skin-type you have. If you have sensitive skin, you will need other products that have less chances of irritating the skin..
A moisturizer (hydrating cream) is the first thing you want to look for. A moisturizer will hydrate the skin and minimize the appearance of fine lines. The most important ingredient of a moisturizer that you use during the day is sunscreen, as this prevents (further) signs of aging. Look for a cream that offers at least SPF30. A moisturizer that you use in the evening, does not need SPF.
The moisturizer can have certain active ingredients (ingredients that work against signs of aging). Retinol is a very effective one, however this ingredient should be avoided when you have sensitive skin. Antioxidants like vitamin C are ingredients that you want to look for when you want to prevent wrinkles.
It is not always true that the most expensive product will work the best; effective products come in all prices.
What exactly are antioxidants, collagen, Q10, retinol and hyaluronic acid?
Certain ingredients are often used in anti-aging products. But what are they exactly and how do they work?
Antioxidants are substances that can prevent or slow the damage caused to the cells by free radicals. Free radicals are molecules that the body produces as a reaction to environmental factors like smoking, sunlight and air pollution. Antioxidants are often found in fruits and vegetables. Most of the antioxidants prevent skin aging, but don’t treat it. The only antioxidant that can treat wrinkles is vitamin C.
Collagen is a protein that provides strength and structure to the skin and occurs in the body naturally. It is broken down over time by free radicals. This process causes wrinkles. Collagen can be added to creams to hydrate the skin and keep it supple, making wrinkles less pronounced. However, collagen in a cream can not undo the natural collagen loss of the skin and make wrinkles disappear.
Q10 is a type of antioxidant that naturally occurs in the body, but decreases with age. It can be found in fish and shellfish. When used in a cream, it can penetrate the skin and make wrinkles less deep, and prevent other signs of aging, like pigmentation.
Retinol is a type of vitamin A. It is an ingredient that accelerates skin renewal and reduces collagen damage. As a result it reduces the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles and age spots. However, this product doesn’t work for everyone. Some people tend to react allergically when they use retinol in a cream.
Hyaluronic acid is also a substance that occurs naturally in the body, and breaks down over time. In a cream, the acid penetrates through the skin and holds onto water to provide radiance and fullness to the skin, and therefore reduces the appearance of wrinkles.
Should I take supplements?
There are some supplements on the market that are advertised to be anti-aging. But what supplements are good, and do you even need them? A healthy, balanced diet with enough vitamins from fruits and vegetables is recommended. These will give you most, if not all necessary vitamins you need. You don’t ‘need’ supplements, however, sometimes they can help with some processes in the body. Based on the nutrients that your diet provides, you can decide to take certain supplements.
In the morning 200mg of coQ10 is recommended to reduce wrinkles in older age. It can also be found in fish and shellfish.
Omega 3 supplements can help hydrating the skin and minimize lines. This healthy fatty acid is not produced by the body so it needs to be acquired from foods like fish, walnuts and flaxseeds.
Vitamin C increases collagen production and can be found in citrus fruits, tomatoes and paprikas.
At what age should I start using anti-aging products?
Prevention is the best thing you can do when it comes to anti-aging treatments. Since the sun is the most important factor contributing to skin aging, it is best to start as early as possible with protecting your skin from the sun. This will not only prevent (further) formation of wrinkles and spots, but also prevent skin cancer.
What treatments are there to treat skin aging?
There are many ways to treat signs of aging. Depending on the kind of signs and the severity, a treatment can be found for almost every issue. A dermatologist will be able to advise you about the options that will suit your skin and wishes. These are the anti-aging treatments we perform at DermoVicenza:
CO2 laser can be used to remove verruca seborrhoica and to treat wrinkles. For maximum effect in the treatment of wrinkles, a TCA peeling can later be applied to the area.
Q-switch Nd:YAG laser can be used to treat pigmented age spots and for biostimulation; a type of peeling that treats fine lines and wrinkles.
Botuline and hyaluronic acid injections to treat wrinkles.
How should I take care of my skin daily?
You can start the day by using a gentle cleanser to cleanse the face, followed by a hydrating cream with at least SPF30 to protect your skin from the sun. If you want, you can now follow with makeup. Apply sunscreen during the day, and don’t forget to also apply sunscreen to the chest, forearms and hands, since these are often exposed to the sun.
In the evening, you can use a micellar water to take off makeup, and use a gentle cleanser to take off the excess dirt. Follow with a hydrating cream.
I have spots on my skin, what can I do about them?
There are some types of spots that develop or increase in older age. Most of them can be treated very easily.
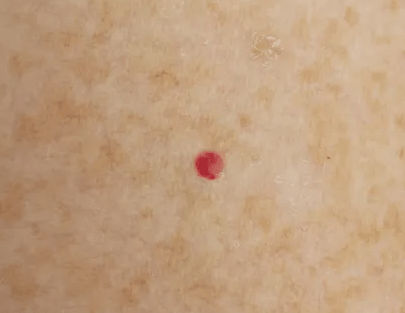
These red spots are called cherry angiomas. They look like red moles because of the collection of blood vessels inside of them. They can be found mainly on the trunk, but also on other regions on the body. They will not go away by themselves. Cherry angiomas are not a cause for concern as long as they don’t bleed or change in size, shape or color. They can be treated with a Diode vascular laser or electrocoagulation.
Senile warts, also known as verruca seborrhoica, are rough and usually elevated dark spots on the skin that increase with age and can develop anywhere on the body, but mainly on the head and trunk. They can easily be removed with electrocoagulation, CO2 laser, cryotherapy or excision.
Sun spots, also called lentigo solaris/senilis, are spots that develop on areas that have been often exposed to the sun, like the hands, underarms, face, chest and shoulders. They can be treated with the Q-switch Nd:YAG laser, that focuses on the darker pigment in the spots.
Skin tags (fibroma molle) are often seen in the neck and armpits, but can develop in other areas. They usually develop as a result of friction and/or irritation of the skin. They can easily be removed with electrocoagulation or a simple excision.
Referenze
(1) Uitto, J. (1997). Understanding premature skin aging. The New England Journal of Medicine. 337(20), 1463-1465.
(2) Baumann, L., & Saghari, S. (2009). Photoaging. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 34-41). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(3) Baumann, L., & Saghari, S. (2009). Cigarettes and Aging Skin. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 42-44). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(4) Baumann, L. (2009). Nutrition and the Skin In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 46-66). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(5) Saghari, S., & Baumann, L. (2009). Wrinkled Skin. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 145-147). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(6) Trookman, N.S., Rizer, R.L., Ford, R., Ho, E., & Gotz, V. (2009). Immediate and Long-term Clinical Benefits of a Topical Treatment for Facial Lines and Wrinkles. Journal of Clinical Aesthetic Dermatology. 2(3), 38-43.
(7) Baumann, L. & Allemann, I.B. (2009). Antioxidants. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 292-311). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(8) Baumann, L., & Saghari, S. (2009). Basic Science of the Dermis. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 8-13). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(9) Phillips C,L., Combs, S.B., Pinnell, S.R. (1994). Effects of ascorbic acid on proliferation and collagen synthesis in relation to the donor age of human dermal fibroblasts. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 103, 228-232.
Il controllo dei "nei"
curato da Anissa Westenberg
Cosa sono i “nei”?
I nei (più correttamente “nevi melanocitici”) sono piccole macchie marrone scuro che si sviluppano quando i melanociti crescono ammassati. I melanociti sono le cellule che danno alla pelle il suo colore. I nei possono svilupparsi in qualsiasi parte del corpo. Cambiamenti ormonali come la pubertà o la gravidanza possono renderli più grandi e / o più scuri.
Esistono diversi tipi di nei e il loro aspetto può essere molto vario. Alcuni sono di colore più scuro, altri sono più chiari. Alcuni sono sollevati sopra la pelle e altri sono piatti. Ci sono anche alcuni che sono blu o hanno un bordo bianco.
La maggior parte delle persone non nasce con nei, solo l'1-3% dei neonati ne ha. Questi sono chiamati nevi congeniti. La maggior parte dei nei sono acquisiti: si sviluppano con l'età, di solito su aree esposte al sole.
La maggior parte dei nei sono innocui, ma c'è la possibilità che evolvano in melanoma. Pertanto è importante tenere d'occhio i nei. Quando un neo sembra diverso dagli altri o presenta uno dei segni ABCDE, dovresti contattare il tuo dermatologo.
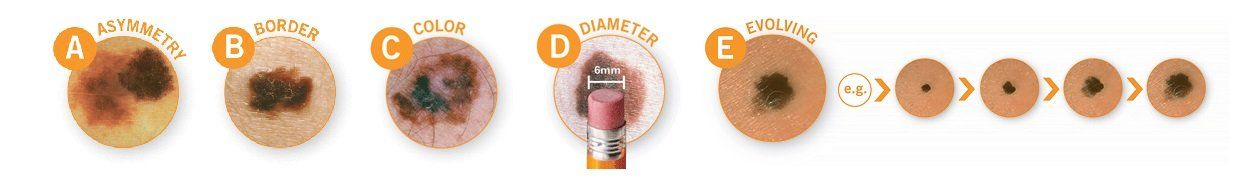
Cos’è la regola ABCDE?
La regola ABCDE è un sistema che è possibile utilizzare per rilevare i cambiamenti dei nei, possibile indizio di melanoma. Ogni lettera rappresenta una caratteristica dei nei da cercare.
Asimmetria: una metà del neo è diversa dall'altra metà.
Bordo: il neo ha bordi irregolari.
Colore: il neo ha cambiato colore o ha molti o colori misti.
Diametro: il neo diventa più grande; più di 6 mm di diametro.
Evoluzione: il neo continua a cambiare in dimensioni, colore, forma o spessore.
Se noti un neo che presenta una o più di queste caratteristiche o se noti che sembra diverso dagli altri nei sul tuo corpo, contatta il tuo dermatologo per segnalare i cambiamenti. (1,2)
Perché ho tanti nei?
La maggior parte dei nei si sviluppa con l'età. Le persone che sono state molto esposte al sole durante la loro vita, avranno più probabilità di acquisire più nei.
Quando le persone hanno meno di 50 anni e hanno più di 20 nei su ciascun braccio, ciò significa che hanno maggiori probabilità di sviluppare il melanoma. Assicurati di controllare spesso i tuoi nei per eventuali cambiamenti se conti più di 20 nei su ciascun braccio. Questo può essere fatto con la regola ABCDE. Inoltre, fai attenzione ai nei che sembrano diversi dagli altri, anche se non soddisfano i criteri ABCDE. Segnala i cambiamenti al tuo dermatologo e assicurati di avere controlli annuali della pelle. (3)
Quando sono pericolosi i nei?
Di solito, i nei non sono pericolosi. Ma a volte possono esserlo, poiché esiste il rischio di sviluppare il melanoma, un cancro della pelle molto pericoloso.
I rischi per lo sviluppo del melanoma sono l'esposizione al sole e le scottature in giovane età, una grande quantità di nei e nevi atipici e congeniti. I nevi atipici sono nei che sembrano diversi da quelli normali. I nevi congeniti sono nei che esistono alla nascita. Tuttavia, solo il 2% delle persone ha nevi congeniti.
I nei che possono svilupparsi in melanoma, di solito sono nuovi e si manifestano in età adulta. Pertanto è importante controllare i nei una volta al mese, soprattutto se ne hai molti. Cerca nei nuovi e nei che cambiano di colore, altezza, forma e/o dimensione o che sembrano diversi dagli altri. Questo può essere fatto con il metodo ABCDE. Segnala eventuali cambiamenti o preoccupazioni al tuo dermatologo. (4,5)
Perché è utile il controllo i nei?
Il controllo dei nei è importante perché possono trasformarsi in cancro della pelle. Il cancro della pelle è il tipo più comune di cancro al giorno d'oggi, 1 persona su 5 ne sarà affetto durante la vita e il numero di diagnosi continua ad aumentare ogni anno.
Il controllo dei nei permette di individuare il melanoma quando è ancora in fase precoce e la sua cura sarà più facile e veloce. Le probabilità di sopravvivenza saranno molto più elevate quando viene trattato in una fase precoce. Il melanoma che viene rilevato in una fase successiva, sarà più difficile da trattare e darà più complicazioni. (6,7)
Quando è necessario fare il controllo dei nei?
Tutti sono a rischio di sviluppare il cancro della pelle, quindi è sempre necessario controllare i nei. Tuttavia, alcune persone hanno un rischio maggiore rispetto ad altre, pertanto, dovrebbero controllare i loro nei più spesso e sono consigliate di sottoporsi a controlli dermatologici cutanei più regolarmente o in età precoce. A tutti consigliamo l’autocontrollo dei nei una volta al mese con il metodo ABCDE. Visita un dermatologo per un controllo annuale della pelle quando hai più di 50 anni o hai uno o più dei seguenti criteri:
Se hai avuto scottature solari in giovane età e molta esposizione (ricreativa) al sole durante la tua vita. Anche i lettini abbronzanti contano.
Più di 20 nei su ciascun braccio, soprattutto al di sotto dei 50 anni.
Se tu o una persona nella tua famiglia ha una storia di cancro della pelle.
In caso di malattie, problemi genetici o uso di farmaci che colpiscono la pelle.
Se sei stato trattato con radiazioni o farmaci immunosoppressori o se hai un sistema immunitario indebolito.
Se hai nevi congeniti (nei da quando sei nato).
Se trovi un neo di cui sei preoccupato, non aspettare la visita annuale ma segnala i cambiamenti il più presto possibile al tuo dermatologo. (3,8)
È vero che i nei vanno protetti dal sole?
Si, come la pelle sana. Proteggere solo i nei non ha senso ed è pericoloso: i melanociti sono anche nella pelle sana, e se si scottano possono sviluppare un melanoma anche dove non c’è un neo.
Le persone con molti nei di solito hanno avuto più esposizione al sole durante la loro vita e un rischio maggiore di sviluppare il cancro della pelle. Pertanto è importante prevenire ulteriori rischi di cancro della pelle, proteggendo il più possibile la pelle dal sole. Ciò è importante soprattutto nei bambini e nei giovani perché le scottature solari in giovane età sono predittive del cancro della pelle più avanti nella vita.
È possibile proteggere la pelle evitando il più possibile la luce solare diretta, in particolare tra le 10:00 e le 16:00. Si consiglia inoltre di applicare una crema solare di almeno SPF30 ogni mattina e di riapplicarla durante il giorno quando la pelle è esposta al sole. Concentrati su aree che sono spesso esposte al sole come viso, petto, spalle e avambracci e non dimenticare aree come naso e orecchie. Proteggere la pelle dal sole impedirà ai nei di diventare più scuri e rallenterà l'invecchiamento cutaneo. (9,10)
Se ho nei posso fare le lampade?
Scoraggiamo fortemente l'uso di lettini abbronzanti per tutti. Il loro uso aumenta il rischio di sviluppare il cancro della pelle, specialmente nelle donne di 45 anni e più giovani.
Un'opzione più sicura che offre un'abbronzatura sana e naturale è l'auto-abbronzatura. Questo può essere fatto con prodotti come lozioni, creme, salviette, spray o mousse, che utilizzano l'ingrediente DHA per colorare temporaneamente le cellule morte sulla superficie della pelle. Una volta che queste cellule si distaccano, il colore scompare e la procedura può essere ripetuta. Assicurati di applicare sempre una crema solare di almeno SPF30 durante il giorno.
Un altro vantaggio dell'utilizzo dell'abbronzatura al posto dei lettini abbronzanti o della luce solare è la prevenzione dell'invecchiamento cutaneo. (11)
Ho grattato un neo e ha sanguinato: è pericoloso?
Proprio come qualsiasi parte della pelle, un neo sanguinerà quando la graffi troppo. I nei possono irritarsi a causa dell'attrito con i vestiti e quindi causare prurito, spingendoti a grattarli. In questo caso, il sanguinamento non è nulla di cui preoccuparsi.
Tuttavia, se il neo prude o sanguina senza motivo, se il sanguinamento non si interrompe o se il neo non guarisce, è necessario contattare il dermatologo. (12)
Cosa posso fare per impedire che compaiano nuovi nei?
I nei si formano a seguito dell'esposizione al sole, pertanto la loro prevenzione può essere effettuata limitando il più possibile l'esposizione al sole. Tuttavia, non puoi prevenire tutti i nei, poiché il sole produce mutazioni nel DNA che non possono essere annullate. Limitare l'esposizione al sole previene ulteriori mutazioni eccessive del DNA.
Puoi proteggere la tua pelle evitando il sole nelle ore di punta, tra le 10:00 e le 16:00. Applicare sempre una crema solare al mattino di almeno SPF30, con protezione UVA e UVB. Devi riapplicare la protezione solare durante il giorno quando sei fuori, perché l'SPF funzionerà con il fattore massimo solo per 2 ore. Assicurati di applicarlo a tutte le aree esposte al sole e presta particolare attenzione al naso e alle orecchie. I tuoi capelli proteggono la maggior parte della testa dal sole, ma se hai capelli più sottili o punti calvi, si consiglia di indossare un cappello.
Oltre alla prevenzione dei nei, la limitazione dell'esposizione solare previene anche l'invecchiamento cutaneo. (9,10)
What are moles?
Moles (also called nevi) are small, dark brown spots that develop when melanocytes grow in clusters. Melanocytes are the cells that give your skin its color. Moles can develop anywhere on the body. Hormonal changes like puberty or pregnancy can make moles larger and/or darker.
There are different types of moles that all look different. Some are darker in color, some are lighter. Some are risen above the skin and some are flat. There are even some that are blue or have a white border.
Most people are not born with moles, only 1-3% of newborn babies have them. Those are called congenital nevi. Most moles are acquired ones: they develop with age, usually on areas that are exposed to the sun.
Most moles are harmless, but there is a chance of them evolving into melanoma. Therefore it is important to keep a close watch on them. When a mole looks different from your other ones or has one of the ABCDE signs, you should contact your dermatologist.
What is the ABCDE rule?
The ABCDE rule is a system that you can use to detect changes in moles that are a possible indication for melanoma. Each letter stands for a characteristic of moles to look out for.
Asymmetry: One half of the spot is unlike the other half.
Border: The mole has irregular borders.
Color: The mole has changed color or has many or mixed colors.
Diameter: The mole gets larger; more than 6mm in diameter.
Evolving: The mole keeps changing in size, color, shape, or thickness.
If you notice a mole that has one or more of these characteristics, or that looks different from other moles on your body, contact your dermatologist to report the changes. (1,2)
Why do I have many moles?
Most moles develop with age. People that had a lot of sun exposure during their lives, have a bigger chance of developing many moles.
When people are younger than 50 and have more than 20 moles on each arm, this means that they have a higher chance of developing melanoma. Make sure to check your moles often for changes if you count more than 20 moles on each arm. This can be done with the ABCDE rule. Also be aware of moles that look different from the other ones you have, even if they don’t meet the ABCDE criteria. Report changes to your dermatologist, and make sure to have annual skin-checks. (3)
When are moles dangerous?
Usually, moles are not dangerous. But sometimes they can be, as there is a risk for developing melanoma; a dangerous type of skin cancer.
Risks for developing melanoma are a lot of sun exposure and sunburn in young age, a big amount of moles, and atypical and congenital nevi. Atypical nevi are moles that look different from normal ones. Congenital nevi are moles that exist at birth. However, only 1-3% of people have a congenital nevi.
Moles that can develop into melanoma, are usually new moles that develop in adult age. Therefore it is important to check your moles once a month, especially if you have a lot of them. Look out for new ones, and moles that change in color, height, shape and/or size, or that look different from the other ones. This can be done with the ABCDE method. Report any changes or worries to your dermatologist. (4,5)
Why is it useful to control moles?
Controlling moles is important because they can turn into skin cancer. Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer nowadays, 1 in 5 people will develop it in their lifetime. And the number of diagnoses keeps increasing each year.
The control of moles makes it possible to identify melanomas in an early stage, which will make treatment easier and quicker. The chances of survival will be a lot higher in this case. Melanoma that is detected in a later stage, will be more difficult to treat and give more complications. (6,7)
When is it necessary to check moles?
Everyone is at risk for developing skin cancer, therefore it is always necessary to check your moles. However, some people have higher risk of developing skin cancer than others. Therefore, they should check their moles more often, and are advised to go to dermatological skin-checks more regularly or on an earlier age. We recommend everyone to check your moles yourself once every month with the ABCDE method. Visit a dermatologist for a yearly skin check when you’re older than 50, or have one or more of the following criteria:
If you had sunburns in younger age, and much (recreational) sun exposure during your lifetime. Tanning beds count as well.
More than 20 moles on each arm, especially below the age of 50.
If you or a person in your family has a history of skin cancer.
If you have any illnesses, genetic problems or use medication that affect the skin.
If you have been treated with radiation or immunosuppressive medication, or if you have a weakened immune system.
If you have congenital nevi (moles since you were born).
If you find a mole that you’re worried about, don’t wait until the yearly visit but report changes as soon as possible to your dermatologist. (3,8)
Is it true that moles should be protected from the sun?
Yes, just like healthy skin. Protecting only the moles doesn’t make sense and can even be dangerous; melanocytes are also present in healthy skin, and when they burn they can develop melanoma, even if there is no mole.
People that have many moles, usually had more sun exposure during their lives, and have a higher risk of developing skin cancer. Therefore it is important to prevent further risk of skin cancer, by protecting the skin from the sun as much as possible. This is important especially in children and young adults, because sunburns in young age are predictive of skin cancer later in life.
Protecting the skin can be done by avoiding direct sunlight as much as possible, especially in between 10AM and 4PM. Besides that it is recommended to apply a sunscreen of at least SPF30 every morning, and to repeat it during the day when the skin is exposed to the sun. Focus on areas that are often exposed to the sun, like the face, chest, shoulders and forearms, and don’t forget areas like the nose and ears. Protecting the skin against the sun can prevent moles from getting darker, and delay skin aging. (9,10)
Can I use sunbeds if I have moles?
We strongly discourage the use of tanning beds for everyone. Using tanning beds increases the risk for developing skin cancer, especially in women of 45 and younger.
A safer option that provides a healthy, natural tan, is self tanning. This can be done with products like lotions, creams, wipes, sprays or mousses, that use the ingredient DHA to temporarily tint the dead cells on the surface of the skin. Once the dead skin cells shed off, the color will disappear and the procedure can be repeated. Make sure to always wear a sunscreen of at least SPF30 during the day.
Another advantage of using self tanning instead of tanning beds or sunlight, is the prevention of skin ageing. (11)
I scratched a mole and it was bleeding, is this dangerous?
Just like any part of your skin, a mole will bleed when you scratch it too much. Moles can get irritated because of friction with clothes and therefore itch, causing you to scratch them. In this case, the bleeding is nothing to worry about.
However, if the mole is itching or bleeds without a reason, if the bleeding doesn’t stop or if the mole doesn’t heal, you should contact your dermatologist. (12)
What can I do to prevent new moles from appearing?
Moles form as a consequence of sun exposure. Therefore, preventing moles can be done by limiting sun exposure as much as possible. However, you can’t prevent all moles, since the sun makes mutations in the DNA that cannot be undone. Limiting sun exposure will prevent further excessive DNA mutations.
You can protect your skin by avoiding the sun during peak hours, in between 10AM and 4 PM. Always apply a sunscreen in the morning of at least SPF30, with UVA and UVB protection. You have to reapply sunscreen during the day when you’re outside, because the SPF will only work with the maximum factor for 2 hours. Make sure to apply it to all areas that are exposed to the sun and pay extra attention to the nose and ears. Your hair protects most of your head from the sun, but if you have thinner hair or bald spots, it is recommended to wear a cap or hat.
Besides prevention of moles, limiting sun exposure will also prevent skin aging. (9,10)
Referenze
(1) Rigel, D.S., Friedman, R.J., Kopf, A.W., & Polsky, D. (2005). ABCDE - An Evolving Concept in the early Detection of Melanoma. Archives of Dermatology. 141(8), 1032-1034.
(2) American Academy of Dermatology Association. (n.d.). Skin Cancer. Retrieved from https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/skin-cancer/find/at-risk/abcdes
(3) Argenziano, G., Giacomel, J., Zalaudek, I., Apalla, Z., Blum, A., De Simone, P., Lallas, A., . . . Kittler, H. (2014). Twenty nevi on the arms: A simple rule to identify patients younger than 50 years of age at higher risk for melanoma. European Journal of Cancer Prevention. 23(5), 458-463.
(4) Pampena, R., Kyrgidis, A., Lallas, A., Moscarella, E., Argenziano, G., & Longo, C. (2017). A meta-analysis of nevus associated melanoma: Prevalence and practical implications. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 77(5), 983-945.
(5) Gandini, S., Sera, F., Cattaruzza, M.S., Pasquini, P., Abeni, D., Boyle, P., & Melchi, C.F. (2005). Meta-analysis of risk factors for cutaneous melanoma, I: common and atypical naevi. European Journal of Cancer. 41(1), 28-44.
(6) Guy, G.P., Thomas, C.C., Thompson, T., Watson, M., Massetti, G.M., Richardson, L.C. (2015). Vital signs: Melanoma incidence and mortality trends and projections - United States, 1982-2030. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 64(21), 591-596.
(7) Stern, R.S. (2010). Prevalence of a history of skin cancer in 2007: results of an incidence-based model. Archives of Dermatology. 146(3), 279-282.
(8) Parkin, D.M., Mesher, D., & Sasieni, P. (2011). Cancers attributable to solar (ultraviolet) radiation exposure in the UK in 2010. British Journal of Cancer. 105, 66-69.
(9) Aalborg, J., Morelli, J.G., Mokrohisky, S.T., Asdigian, N.L., Byers, T.E., Dellavalle, R.P., Box, N.F., & Crane, L.A. (2009). Tanning and increased nevus development in very-light-skinned children without red hair. Archives of Dermatology. 145(9), 989-996.
(10) Baumann, L., & Saghari, S. (2009). Photoaging. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 34-41). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill.
(11) Colantonio, S., Bracken, M.B., & Beecker, J. (2014). The association of indoor tanning and melanoma in adults: systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 70, 847-857.
(12) American Academy of Dermatology Association. (n.d.). Melanoma. Retrieved from https://www.aad.org/media/stats-melanomaNuovo paragrafo
La caduta dei capelli
curato da Anissa Westenberg
Perché in autunno perdo molti capelli?
Alcune persone sperimentano più perdita di capelli in determinate stagioni, in particolare durante l'autunno. Ciò può essere spiegato dal ciclo di crescita naturale dei capelli. Le fasi di questo ciclo sono l'anagen (fase di crescita), catagen (fase di transizione) e telogen (fase di riposo). Dopo aver raggiunto la fase telogen, i capelli cadranno naturalmente.
Intorno a settembre, anche come conseguenza del caldo e del sole dell’estate, vi è la percentuale maggiore di capelli nella fase telogen, il che significa che presto cadranno, per lasciare crescere nuovi capelli. Verso marzo la maggior parte dei capelli sarà in fase anagen. Può esserci anche caduta del pelo senza nuovo pelo, fase exogen; non sembra però essere frequente.
La perdita di capelli stagionale non è nulla di cui preoccuparsi. È normale perdere circa 100-150 capelli al giorno. Se sei ancora preoccupato o pensi che potresti perdere molti di più, contatta il tuo dermatologo. (1,2)
Perché I miei capelli diventano sempre più sottili?
Il diradamento e la caduta dei capelli sono due cose diverse.
Il diradamento dei capelli è un processo che spesso arriva naturalmente con l'età, ed è un processo graduale. Può essere aggravato da fattori come l'inquinamento, la tinta e il danneggiamento dei capelli e l'uso di prodotti sbagliati. Ciò si traduce in capelli più deboli, più fragili e con meno volume. Per ridurre al minimo il diradamento dei capelli, evitare spazzolatura, asciugatura e styling costanti. Una dieta con abbastanza nutrienti da frutta e verdura può aiutare a rafforzare i capelli. Può anche essere un segno di calvizie, soprattutto femminile.
La perdita dei capelli ha molto a che fare con la genetica e gli ormoni. È normale perdere fino a 100-150 capelli al giorno. A causa dell'invecchiamento e dei cambiamenti ormonali, questo numero può aumentare. Anche le condizioni mediche, i farmaci, la dieta e lo stress possono peggiorarlo. Quando perdi ciuffi di capelli, o molti capelli ti rimangono nelle mani quando te le passi tra i capelli, potrebbe essere un segno di eccessiva perdita di capelli. Contatta il tuo medico in questo caso. (2)
Cosa posso fare per fermare la caduta dei capelli?
La perdita dei capelli può verificarsi per molte ragioni diverse. Alcune sono ormonali, mentre a volte possono esserne causa fattori come lo stress o la dieta. Pertanto, alcuni tipi di perdita di capelli sono difficili da fermare, ad esempio quella dovuta all'invecchiamento. Ci sono alcune cose che puoi fare per ridurre al minimo la perdita di capelli.
È dimostrato che il fumo peggiora la caduta dei capelli. Se fumi e avverti una perdita di capelli, è meglio smettere. Ciò migliorerà anche la salute generale.
La dieta può causare la caduta dei capelli in caso di carenza di zinco e / o ferro. Ciò può verificarsi nei vegetariani, poiché la dieta vegetariana ha naturalmente meno zinco. Gli integratori di questi minerali possono aiutare a risolvere questa carenza. Anche il digiuno estremo e le diete crash possono causare la caduta dei capelli.
Alcuni tipi di acconciatura possono danneggiare i capelli, rendendoli più fragili e più facili da spezzare. Evitare il calore, l'uso eccessivo di prodotti, tirare i capelli (code di cavallo strette) e spazzolare in eccesso.
Lo stress estremo può causare o aggravare la caduta dei capelli. Di solito i capelli cadono 2 mesi dopo che una persona sperimenta molto stress. Successivamente, la caduta dei capelli può causare stress e può quindi svilupparsi un circolo vizioso. Cerca di evitare il più possibile lo stress e cerca l'aiuto di un dermatologo per interrompere questo ciclo.
Il minoxidil può essere acquistato al banco in lozioni o shampoo. Si è dimostrato efficace per la ricrescita dei capelli. Si raccomanda una percentuale del 2-5% per gli uomini e del 2% per le donne.
Non aspettarti una crescita dei capelli istantanea. Potrebbero essere necessari diversi mesi per cambiamenti visibili nella crescita dei capelli. Se non noti miglioramenti dopo questo periodo e/o sei preoccupato per la caduta dei capelli, contatta il tuo dermatologo per discutere delle opzioni. (2,3)
Ho pochi capelli e tanti peli, perché?
Questo fenomeno ha a che fare con gli ormoni. Il testosterone, l’ormone maschile, ha un sottoprodotto chiamato diidrotestosterone (DHT). Il DHT è responsabile di molte caratteristiche che si sviluppano durante la pubertà, come i capelli scuri terminali sul viso e sul corpo. Nel tempo, i follicoli piliferi diventano più sensibili al DHT, causando la crescita dei peli sul corpo ma i follicoli piliferi sul cuoio capelluto si restringono e muoiono. Ciò significa che più testosterone ha una persona, più peli sul corpo e meno capelli avrà.
Poiché gli uomini hanno molto più testosterone (e quindi DHT) rispetto alle donne, gli effetti saranno molto più importanti. Tuttavia, livelli più elevati di DHT nelle donne possono causare, come negli uomini, la perdita dei capelli sul cuoio capelluto e la crescita dei peli sul corpo, ad esempio nelle donne che hanno la PCOS (Sindrome dell'Ovaio Policistico).
La finasteride è un farmaco su prescrizione che impedisce al testosterone di produrre DHT e contribuirà quindi a prevenire la caduta dei capelli sul cuoio capelluto. Parla con il tuo dermatologo sulle possibilità di trattamento. (4,5)
Uso lozioni e shampoo costosi eppure non vedo miglioramenti, perché?
Il prezzo elevato di un prodotto non significa sempre che il prodotto sia efficace. Questo non significa che dovresti scegliere il prodotto più economico che puoi trovare: questi prodotti spesso hanno filler (ingredienti inutili) che possono irritare la pelle e aggravare i problemi. Gli ingredienti efficaci nei prodotti sono molto importanti.
Per trattare la caduta dei capelli, è possibile utilizzare una lozione con Minoxidil. Questo può essere acquistato al banco ed è stato dimostrato essere il prodotto più efficace nella stimolazione della crescita dei capelli. Una percentuale del 2-5% è consigliata per gli uomini e il 2% per le donne. (2,6)
In gravidanza avevo bei capelli poi con l’allattamento ne ho persi molti, perché?
Durante la gravidanza il corpo produce molto ormone femminile: estrogeno. Questo ormone ha molte funzioni importanti durante la gravidanza, ma ha anche un effetto sui capelli. L'estrogeno aumenta la quantità di tempo che i capelli trascorrono nella fase di crescita (anagen) e quindi impedisce loro di cadere. Questo è il motivo per cui molte donne hanno i capelli più lunghi e pieni durante la gravidanza. Dopo il parto, c'è un grande calo dei livelli di estrogeno e tutti i capelli che sarebbero dovuti cadere durante la gravidanza lo faranno ora.
Gli ormoni prodotti durante l'allattamento sopprimono ulteriormente la produzione di estrogeno, causando la caduta di più capelli.
Quando i livelli di estrogeni tornano stabili dopo gravidanza e allattamento, i capelli torneranno a crescere normalmente. Tuttavia, questo processo potrebbe essere lento. (4)
La pillola anti-concezionale è pericolosa per i capelli?
La pillola rilascia ormoni nel corpo. Poiché il ciclo di crescita dei tuoi capelli è influenzato dagli ormoni, questo può influenzarli. Il grado di influenza dipende molto dal tipo di pillola, dalla sensibilità dei follicoli piliferi e da come il corpo reagisce alla pillola.
Alcuni tipi di pillola anticoncezionale possono aumentare i livelli di androgeni e innescare o peggiorare la caduta dei capelli.
Altre pillole possono rallentare il processo di diradamento dei capelli e renderli più pieni, aumentando i livelli di estrogeni e/o diminuendo i livelli di testosterone.
La perdita dei capelli può verificarsi anche dopo aver smesso di prendere la pillola, a causa dei cambiamenti ormonali. Qualsiasi farmaco o terapia che può cambiare gli ormoni di una donna può scatenare la caduta dei capelli. Se hai una storia familiare di perdita di capelli ormonale, è meglio scegliere una pillola che contenga livelli più alti di estrogeno. Un medico sarà in grado di aiutarti a scegliere la pillola corretta. (7)
Mi è comparsa una chiazza senza capelli: cosa può essere?
Ci sono diverse cause per le chiazze calve sulla testa.
La tinea capitis (tigna) è un'infezione fungina del cuoio capelluto, che provoca chiazze calve con scaglie. L'alopecia triangolare temporale provoca una chiazza calva alle tempie ed è più comunemente osservata nei bambini. L'alopecia areata inizia con chiazze calve circolari o irregolari. È una malattia in cui il sistema immunitario attacca i follicoli piliferi.
Contatta il tuo dermatologo quando trovi chiazze senza capelli. Un medico sarà in grado di dirti che tipo di perdita di capelli hai e come trattarla.
Si sono diradati i capelli alle tempie, perché?
La perdita dei capelli alle tempie si vede spesso negli uomini, ma non è insolita nelle donne. Può verificarsi come parte del processo naturale di invecchiamento. Questo tipo di perdita di capelli è legata agli ormoni androgeni, che si verificano sia negli uomini che nelle donne. Con l'età, l’attività relativa degli androgeni aumenta e questo può portare a un ciclo più breve di crescita dei capelli, ciocche più sottili e più corte e una crescita ritardata di nuovi capelli. L'età di insorgenza e la quantità di perdita di capelli dipendono principalmente dalla genetica, quindi è difficile da prevenire. Per trattare la caduta dei capelli, è possibile utilizzare 1-2 volte al giorno una lozione o una mousse con minoxidil. Gli uomini possono usare 2-5% di minoxidil, le donne non devono usarne più del 2%. Questo prodotto stimola i follicoli piliferi ad entrare nella fase di crescita. Un'altra opzione può essere la finasteride, un farmaco su prescrizione. Parla con il tuo dermatologo sulle opzioni per il trattamento. (2,6,8,9)
Why do I lose more hair in fall?
Some people experience more hair loss in certain seasons, in particular during fall. This can be explained by the natural hair growth cycle. The phases of this cycle are the anagen (growth phase), catagen (transitional phase) and telogen phase (resting phase). After the hair reaches the telogen phase, it will naturally fall out. Around September, also as a consequence of the heat and the sun, most hairs are in the telogen phase, which means they will soon fall out to let new hairs grow. After this, new hairs will grow and around March most hairs will be in the anagen phase. Sometimes hair loss without growth of new hairs occurs, it is called the exogen phase. This, however, does not frequently happen.
The seasonal hair loss is nothing to worry about. It is normal to lose around 100-150 hairs per day. If you are still worried, or you think you might be losing a lot more hair, contact your dermatologist. (1,2)
Why is my hair getting thinner?
Hair thinning and hair loss are two different things.
Hair thinning is a process that often comes naturally with age, and is a gradual process. It can be aggravated by factors like pollution, dyeing and damaging hair and using wrong products. This results in weaker, more fragile hair with less volume. To minimize hair thinning, avoid constant brushing, blow-drying and styling. A diet with enough nutrients from fruits and vegetables can help strengthening the hair. Hair thinning could also be a sign of baldness, mainly in women.
Hair loss has a lot to do with genetics and hormones. It is normal to lose up to 100-150 hairs a day. Because of aging and hormonal changes, this number can increase. Also medical conditions, medication, diet and stress can worsen it. When you start to lose clumps of hair, or a lot of hair comes out when you run your fingers through it, it could be a sign of excessive hair loss. Contact your doctor in this case. (2)
What can I do to stop hair loss?
Hair loss can occur for a lot of different reasons. Some are hormonal, while sometimes factors like stress or diet cause it. Therefore, some kinds of hair loss are difficult to stop, for example hair loss that comes with aging. There are a few things you can do to minimize the amount of hair loss.
Smoking is proven to worsen hair loss. If you smoke and experience hair loss, it is best to quit. This will also improve overall health.
Diet can cause hair to fall out, when there is a deficiency of zinc and/or iron. This can occur in vegetarians, since the vegetarian diet naturally has less zinc. Supplements of these minerals can help solving this deficiency. Also starvation and crash dieting can trigger it.
Certain ways of hairstyling can damage the hair, making it more fragile and break off. Avoid heat, excess use of hair products, pulling the hair (tight ponytails) and excess brushing.
Extreme stress can cause or aggravate hair loss. Usually hair will fall out 2 months after a person experiences a lot of stress. Next, hair loss can cause stress and a vicious cycle can develop. Try to avoid stress as much as possible, and seek help from a dermatologist to break this cycle.
Minoxidil can be bought over the counter in lotions or shampoos. It is proven to be effective for hair regrowth. A percentage of 2-5% is recommended for men, and 2% for women.
Don’t expect hair growth overnight. It might take several months for visible changes in hair growth. If you don’t notice improvement after this period, and/or you are worried about the hair loss, contact your dermatologist to discuss options. (2,3)
Why do I have little hair on my scalp, but lots of body hair?
This phenomenon has to do with hormones. The ‘male hormone’ testosterone has a by-product called dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is responsible for a lot of characteristics that develop during puberty, like darker terminal hair on the face and body. Over time, the hair follicles get more sensitive to DHT, causing hair on the body to grow but hair follicles on the scalp to shrink and die. This means that the more testosterone a person has, the more body hair and less scalp hair he will have.
Since men have a lot more testosterone (and therefore DHT) than women, the effects of it will be a lot more prominent in men. However, higher levels of DHT in women can also cause hair loss on the scalp and hair growth on the body, for example in women who have PCOS (PolyCystic Ovarian Syndrome).
Finasteride is a prescription medication that prevents testosterone from producing DHT, and will therefore help preventing hair loss on the scalp. Talk to your dermatologist about the possibilities for treatment. (4,5)
I use expensive lotions and shampoos, why do I not see improvement?
A high price of a product does not always mean that the product is effective. This doesn’t mean that you should go for the cheapest product you can find: these products often have fillers (useless ingredients) that can irritate the skin and aggravate issues. The effective ingredients in the products are very important.
To treat hair loss, a shampoo or lotion with Minoxidil can be used. This can be bought over the counter, and is proven to be the most effective product that stimulates hair growth. A percentage of 2-5% is advised for men, and 2% for women. (2,6)
During pregnancy I had beautiful hair but during breastfeeding I lost it, why?
During pregnancy the body produces a lot of the female hormone: estrogen. This hormone has a lot of important functions during pregnancy, but also has an effect on the hair. Estrogen increases the amount of time that hair spends in the growing (anagen) phase, and therefore prevents it from falling out. This is the reason a lot of women have fuller, longer hair during pregnancy. After giving birth, there is a big decline in estrogen levels, and all the hair that should have fallen out during pregnancy, will fall out now.
Hormones produced during breastfeeding will further suppress the production of estrogen, causing more hair to fall out.
When estrogen levels become stable again after pregnancy and breastfeeding, the hair should start growing normally again. However, this process may be slow. (4)
Is the anti conception pill dangerous for hair?
The anti conception pill releases hormones in the body. Because the growth cycle of your hair is influenced by hormones, this can have an influence on your hair. The amount of influence depends a lot by the kind of pill, the sensitivity of your hair follicles and how your body reacts to the pill.
Some types of birth control pills can raise the androgen levels, and trigger or worsen hair loss.
Other pills can slow down the thinning process of the hair and making it seem fuller, by increasing estrogen levels and/or decreasing testosterone levels.
Hair loss can also occur after quitting the pill, because of the hormonal changes. Any medication or therapy that can change a woman’s hormones can trigger hair loss. If you have a family-history of hormonal hair loss, it is best to choose a pill that contains higher levels of estrogen. A doctor will be able to help you choose the right birth control pill. (7)
I found a patch without hair, what can it be?
There are several causes for bald patches on the head.
Tinea capitis (ringworm) is a fungal infection of the scalp, that causes bald patches with flakes. Temporal triangular alopecia causes a bald spot at the temples, and is most commonly seen in children. Alopecia areata starts with circular or patchy bald spots. It is a disease in which the immune system attacks the hair follicles.
Contact your dermatologist when you find patches without hair. A doctor will be able to tell you what type of hair loss you have and how to treat it.
Why do I have hair loss at my temples?
Hair loss at the temples is a type of pattern hair loss that is often seen in men, but is also not unusual in women. It can occur as a part of the natural ageing process. This type of hair loss is linked to androgen hormones, that occur both in men and women. With age, the relative activity of androgens increase and this can lead to a shorter cycle of hair growth, finer and shorter hair strands and delayed growth of new hair. The age of onset and amount of hair loss mainly depends on genetics, therefore it is difficult to prevent. To treat the hair loss, a lotion or mousse with minoxidil can be used 1-2 times a day. Men can use 2-5% minoxidil, women should use not more than 2% minoxidil. This product stimulates the hair follicles to go into the growth phase. An other option can be the prescription medication finasteride. Talk to your dermatologist about options for treatment. (2,6,8,9)
Referenze:
(1) Randall, V.A., & Ebling, F.J.G. (1991). Seasonal changes in human hair growth. British Journal of Dermatology. 124, 146-151.
(2) Harrison, S., & Bergfeld, W. (2009). Diffuse hair loss: Its triggers and management. Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. 76(6), 361-376.
(3) Freiman, A., Bird, G., Metelitsa, AI, Barankin, B., & Lauzon, G.J. (2004). Cutaneous effects of smoking. Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 8(6), 415-423.
(4) Zaulyanov-Scanlan, L. (2009). Hormones and Aging Skin. In L. Baumann, S. Saghari, & E. Weisberg (Ed.), Cosmetic Dermatology - Principles and Practice (2nd ed.) (pp. 29-33). New York, United States: McGraw-Hill
(5) Iamsumang, W., Leerunyakul, K., & Suchonwanit, P. (2020). Finasteride and Its Potential for the Treatment of Female Pattern Hair Loss: Evidence to Date. Drug Design, Development and Therapy. 14, 951-959.Nuovo paragrafo